In accordance with Chinese tax legislation, every company operating a subsidiary in the country is obligated to fulfill monthly tax filings and other related requirements. Compliance with local standards for tax legislation is imperative to maintaining control and minimizing risk for your business in China. This article will go over the primary types of applicable tax rates in China to companies operating in the region, notably, income tax, corporate tax and value-added taxes (VAT).
Income Taxes in China
All individuals currently residing in China or have income derived from the country are required to fulfill tax requirements in accordance with national policies. Based on the time spent in China, individuals are regarded as tax residents or non-residents, with each group being subject to different tax obligations.
Individuals who have resided in China for 183 days or more within a calendar year are considered to be tax residents while those who have spent less than 183 days are classified as non-residents.
Non-residents are only required to fulfill tax obligations on income derived from China, while tax residents are subject to taxes on their worldwide income.
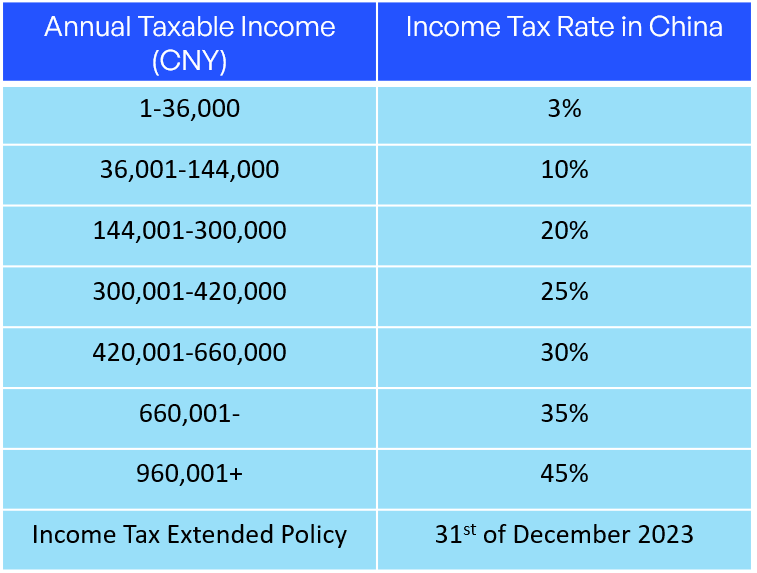
Individual income tax rates in China follows a progressive system based on an employee’s salary. Employers have the responsibility to withhold taxes and make monthly payments on the 15th of each month. The table below underscores the tax rates corresponding to different wage levels, with ranges from 3% to 45%:
The preferential income tax policy, which has allowed foreign employees to benefit from supplementary tax-deductibles, has been extended until the 31st of December 2023. Relevant cost coverages included areas such as children’s education, rental expenses, and aid with critical illnesses.
To calculate your income tax in China, check out our 2024 income tax calculator.
Payment Procedures and Filing Requirements
Foreigners employed in China are required to register with the local tax bureau and submit the applicable forms, passport information and provide detailed certification on their amount of compensation.
Tax filings are generally processed through the payroll under a withholding system, however the individual recipient of income bears full responsibility for paying income taxes.
Taxpayers are required to file income tax returns on a monthly basis, and pay applicable taxes to the local tax bureau, regardless of their source of income and whether or not their income was processed through a withholding system.
Corporate Income Taxes in China
Direct taxes on corporations are generally based on net income generated annually following deductions of any relevant operating costs and losses. Corporate income taxes in China follow either a quarterly or annual settlement schedule, and all amounts adjusted or refunded are moved forward to the next financial year. Applicable tax rates are derived from a company’s net profits.
Who Qualifies as a Chinese Corporate Taxpayer
Companies are categorized as either a resident enterprise or a non-resident enterprise when being considered for corporate income tax. Enterprises established in accordance with both Chinese law and foreign law are regarded as resident enterprises and are under the administration of a Chinese institution.
Enterprises set up in accordance with foreign law and are not under administrative control in China but have either institutions or establishments that have generated income or that are based in China are regarded as non-resident enterprises.
The primary distinction between payable corporate income tax rates between residents and non-resident enterprises is that resident enterprises are taxable on worldwide income while non-resident enterprises are only taxed on China-sourced income.
For any related Chinese establishments tied to non-resident enterprises, any China-sourced income is also taxable. For both foreign and domestic enterprises, corporate income taxes are applied towards profits at a rate of 25%. The applicable CIT rate for non-resident enterprises without establishments in China are taxed at a rate of 20% on their income derived in the country.
To see who qualifies for corporate income tax deductions view our full article on Corporate Income Tax in China.
How Do You Calculate Corporate Income Taxes
Corporate Income Tax Payable Formula:
CIT Payable =
CIT Taxable Income * Applicable Tax rate – Tax Exemptions or Reductions (if applicable)
Taxable Income for CIT in China is derived from the following formula:
CIT Taxable Income =
Total Annual Income – Expenses/Costs – Carry Forward Losses
VAT in China
The introduction of a single value added tax (VAT) system for goods and services has been one of the most notable changes to China’s tax system in recent years.
As a percentage to the sale and import of goods as well as provision of services in or to China, VAT is applied as a percentage. Companies are required to file VAT on a monthly or quarterly basis while normal taxpayers are required to submit filings for VAT every month. Small-scale taxpayers, however, are only required to submit VAT filings on a quarterly basis.
In the near future, further reforms are expected to VAT in China, given that the draft VAT law is pending approval by the National People’s Congress and State Council, will have authority in enacting formal VAT legislation.
Tax-payer Categories
As previously mentioned, VAT is applicable to two groups of taxpayers, notably general and small-scale taxpayers. In terms of the general threshold for income that separates taxpayers into different groups, the amount is RMB 5 million for a general taxpayer, which companies below this threshold will be considered as a small-scale taxpayer. Despite this, companies with sales levels below the threshold are still eligible to apply for general taxpayer status.

VAT China Frequently asked Questions
In light of the constantly changing tax and regulatory environment, and in an effort...
Read moreDo You Understand How Taxes in China Work?
Ensuring compliance with tax obligations in China is fundamental to operating a business in China. The complexities of China’s tax laws and systems in which local organizations must follow can be overwhelming and challenging to navigate for new businesses.
MSA has assisted foreign companies with corporate set-up, accounting and financial advisory support for many years and can help you overcome any barriers to successfully launching your business in China. Get in touch with us and let us assist you right away!