A trademark represents, identifies, and differentiates a brand from others. It protects the image and intellectual property of a business from infringement. Trademarks are invaluable assets that make it easy for customers to identify and find the products or services of a business.
China has one of the biggest consumer markets globally, which is no wonder why international companies want to penetrate its huge potential for expansion and profit. If you are planning to expand into China, learning how the trademark process works is vital to your business growth and the protection of your business’s identity.
Trademark in China
According to the China Trademark Law, any sign, including words, devices, letters, numerals, three-dimensional signs, a mixture of colors, sounds, or a combination of any of these, can be registered as a trademark to distinguish the products and services of a person or organization.
In China, a first-to-file policy is in effect. It grants exclusive rights to registrants who applied first for the trademark, and they receive legal protection of the highest degree for its exclusive use in the country.
Trademark Registration Requirements
There are four aspects that you should satisfy first to be eligible to register a trademark in China:
- Legal – It cannot be the same as or similar to the name or flag of a country or international organization. It also must not discriminate against nationality or promote exaggerated or fraudulent advertising.
- Unique – It should not be the same as or similar to existing trademarks and must be easily distinguishable from the brand of other providers of goods or services.
- Functional – It must not refer to the nature of the product or the product itself. For instance, a company selling apples cannot register either the image of the apple or trademark ‘apple’ because it’s a generic name publicly used by everyone. Also, it cannot sabotage other trademarks by making it confusing for consumers to differentiate yours from other brands.
- Available – The trademark should be available and not yet in the China Trademark Office (CTMO) database.
Trademark Registration Process in China
Registering a trademark in China takes longer compared to other countries. You will have to go through the following processes:
- Determine if your trademark is already registered. You can search the CTMO official website for similar trademarks, get comprehensive information on different trademarks, monitor the status of trademark applications, and stay up to date with new regulations and announcements on new trademarks.
- Submit your application form and other required documents to the State Administration for Industry and Commerce (SAIC).
- The SAIC will review your application and decide whether you can proceed, resolve issues, or provide other requirements. If confirmed to proceed, the SAIC will process the registration of the trademark.
- The SAIC will issue the trademark, and you will receive a certificate of approval.
The whole process takes approximately 12 to 16 months, depending on if the application requirements are met or whether you are required to submit further documentation. It will take longer to process the application if there are issues that arise during the application, such as bad faith trademark registration.
In case you are refused to use a particular trademark applied for, you can contact the TRAB (Trademark Review and Adjudication Board) for an appeal. The TRAB will handle the opposition, and the process can last for up to 12 months.
If you have no previous experience with trademark registration in China, it is best to work with a trademark agency to help with your registration. Should any dispute or problem arise during the application, they can help file the necessary documents and take care of the other processes that could delay the registration.
Keep in mind that you can only utilize the services of a Chinese trademark agency to handle the processing on your behalf, as the application is required to be written in Chinese.
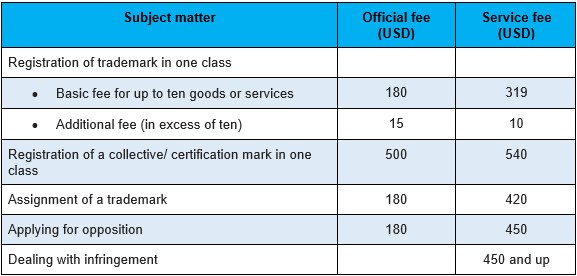
Patent Application Fees
When registering a trademark, you will have to pay the following fees:
These are the minimum expenses you will usually face if you want to register a trademark in China. The cost will increase if you are opposing a bad faith trademark registration.
Validity Period for Trademarks in China
Local and international trademark registrations are valid for 10 years. Renewal of a trademark should be filed six months before its expiration, which will extend its validity for another 10 years. Failure to renew the trademark will result in its automatic cancellation.
If the trademark is not used for commercial purposes within three years, you may lose its validity. Then, the trademark will again be available to those who want to register it.
Do Trademarks Need to be Registered in Chinese Characters?
You will be required to choose a Chinese trademark that sounds and translates meaningfully for your brand. There are two options to choose from when translating your trademark:
- Phonetic Translation
This is for creating a Chinese name that sounds similar to the original English name of the trademark. It is best if the translated name means something positive in the Chinese language.
The best examples of successful phonetic translations are ‘Kou Ke Ke Le’ (Coca Cola), Wò’ērwò (Volvo), Àodí (Audi), and Bēnchí (Benz).
- Literal Translations
This is about choosing a Chinese name that corresponds best to the meaning of the trademark in its original English form. It does not have to sound the same when pronounced, but it should literally translate and pertain to the brand.
For instance, Microsoft is called Wei Ruan, which is the literal translation of the trademark. Apple is called ‘Ping guo’, which directly translates to ‘apple’ in the Chinese language.
What is a Bad Faith Registration Trademark in China?
A trademark is said to be registered in bad faith when it has been registered with the intent of profiting or seeking a ransom from the true owner of the trademark. A common example of bad faith trademark registration in China is by selling counterfeit goods under the trademark of another brand.
Another instance is by registering the trademark and selling it to its foreign owner for a profit. Regardless of the situation, true owners of the trademark have to challenge those who registered their brands in bad faith, which can be a lengthy, costly, and time-wasting process.
Bad faith trademark registrations can happen anywhere in the world, but China is known for this practice because of its trademark law. Unlike in the US and in other countries where a ‘first-to-use’ rule is used, China enforces a ‘first-to-file’ policy on trademarks. This gives people the opportunity to register foreign trademarks and hold them as a hostage before the rightful owners even before the ‘true owner’ has had a chance.
Case Study – Major Companies that had Problems with Trademark Registration
Even big companies are not safe from becoming victims of bad faith trademark registration.
Apple, for example, lost a trademark battle in China when they found out that the local business Xintong Tiandi known for selling handbags and other leather products had already been trademarked “IPHONE.” The court ruled against Apple after it failed to prove that it was the more known brand in China before Xintong Tiandi registered the trademark in 2007.
Facebook also lost a trademark battle when Dr. Su filed for the name first in 2006. The company lost the trademark battle for more than a decade. Facebook also opposed another drinks and beverage company named ‘face book’, but eventually won in 2016.
Final Thoughts
When filing for a trademark in China, it is best to map out your intentions and plan ahead. Bad faith trademark registration is not uncommon in the country, so if you plan to expand into the Chinese market, you should establish a timeline and make sure that no one will file for the same trademark ahead of you. Working with a Chinese trademark agency or legal partner will make the whole process easier for your business.
We Assist with Your Business Needs
We have helped companies to expand to and setup in China for more than a decade. With our long list of clients, we have been committed to delivering the highest quality services, which is what allows us to maintain our strong reputation in the Chinese market. We have assisted small business to large corporations with their setup needs, accounting services, tax advice and more. Get in touch with us right away and let us help you with your business needs in China.