A primary objective for foreign companies in China to manage compliance is to maintain control over their Chinese operations and prevent any negative impact which may arise from non-compliance. To achieve this objective, foreign-invested enterprises with Chinese operations should develop a thorough understanding of Chinese legislation. A thorough understanding of Chinese compliance requirements will not only minimize risks but helps to foster trust between consumers and businesses. Particularly in light of China’s ongoing efforts to implement the Corporate Social Credit System, compliance is more important than ever.
After a foreign investor has legally established a subsidiary in China and obtained its business license it is required to complete several administrative and compliance requirements on a monthly, quarterly and annual basis. More specifically, foreign-invested enterprises in China are required to maintain a reliable record of accounts, must submit tax filings (for among others Corporate Income Tax (CIT), Value Added Tax (VAT), Individual Income Tax (IIT) and Surtaxes), and contribute to social security insurances and the housing provident fund.
In this article, we provide an overview of the essential compliance requirements for foreign companies with operations in China.
When do Compliance Requirements for Foreign Companies come into play?
According to PRC Law, any foreign-invested enterprise in China is required to commence with its basic tax registrations within 30 days of the issuance of the company’s business license. As a consequence, the Chinese subsidiary must complete the prescribed administrative- and tax compliance requirements after completion of the company’s tax registrations.
Compliance requirements in China can be divided into those which must be completed on a monthly, quarterly and annual basis. Here it is important to note that in the month in which tax registrations are completed the Chinese subsidiary is obliged to complete relevant filings regardless of any business activities having taken place, this is called ‘zero-filing’.
China’s Monthly Compliance Requirements
All companies in China must maintain a reliable record of accounts in line with the Chinese Accounting Standards (CAS), also known as the Chinese Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (PRC GAAP). The Chinese Accounting Standards stipulate that accounting should be based on an accrual basis for for-profit enterprises and foreign companies must submit on a monthly basis their Balance Sheet and Income Statement to the in-charge tax authority when completing its monthly tax filings (for more information on accounting in China, please read our full article).
Chinese subsidiaries of foreign companies which are registered as General VAT Taxpayer must complete monthly VAT- and Surtax filings. Companies employing individuals are required to withhold IIT on behalf of their employees on a monthly basis (in our IIT article we explain all important aspects of IIT for foreign companies in China). Furthermore, large enterprises may choose to complete provisional CIT filings on a monthly basis instead of a quarterly basis (for a complete overview of CIT requirements in China, please our read article explaining the essentials of CIT in China). The monthly tax filing deadline in China for foreign companies regarding the aforementioned taxes is the 15th of the next subsequent month (i.e. the tax filing deadline for the month of February is March 15th).
In addition to the monthly IIT filing, companies employing individuals must also make contributions to social security insurances and the housing provident fund every month. In general, contributions for these social securities must be declared and paid before the 10th of the subsequent month. Foreign employees have been required to participate in the Chinese social security system as of 2011, however, since the system is administered at the local level there are some differences between cities. For example, as an exception foreign employees and their employers in Shanghai are currently exempted from making social security and housing fund contributions (for further details on China’s social security system, read our full article).
Please note that the Chinese taxation system is administered at the local level, and as a result relevant tax filing deadlines may differ per locality and are subject to notice from the local in-charge tax authorities. The monthly tax filing deadlines may also be altered due to public holidays and pending notification from the tax authorities.
Quarterly Compliance Requirements in China
Although Small-scale Taxpayers may also elect to complete VAT filings on a monthly basis, they are legally required to complete filing for VAT and Surtaxes on a quarterly basis. Moreover, SMEs in China are required to complete CIT filings on a quarterly basis.
The quarterly tax filing deadline occurs on the 15th of the subsequent month following the end of the quarter (i.e. the tax filing deadline for Q1 (the period of January 1st until March 31st) is April 15th).
Annual Statutory Compliance Requirements
According to Chinese law, all foreign-invested enterprises in China must undergo several annual statutory requirements, which can be divided into the following types:
- A year-end statutory audit (by a qualified CPA);
- An annual Corporate Income Tax Filing;
- Publishing of the annual publication report.
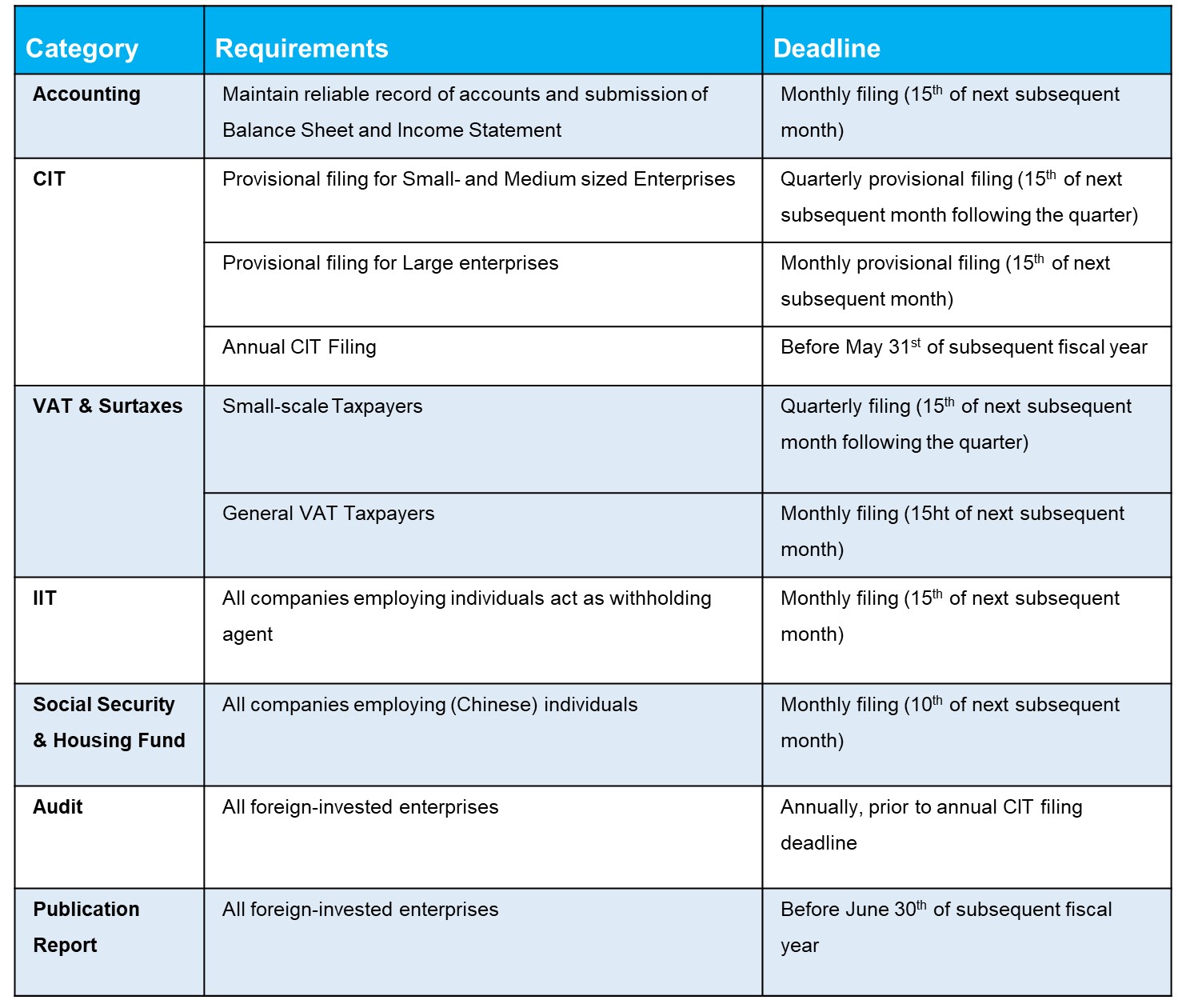
Overview of China Compliance Requirements
In the table below we provide a summary of compliance requirements in China and an overview of key deadlines with which foreign companies must comply:
Conclusion
It is important for the management of foreign companies with subsidiaries in China to thoroughly understand the administrative- and compliance requirements they must meet in order to avoid unnecessary risks and potential adverse consequences to their operations. If foreign companies are unfamiliar with Chinese compliance requirements, they may seek advice from well established third-party service providers.
We support foreign companies throughout all provinces of China to meet the monthly, quarterly and annual compliance requirements and advise on potential risks. If you require any support in light of administrative- of taxation compliance, please do not hesitate to contact us.